Security
This document provides an overview of Dragonfly security considerations. Dragonfly security features provide strong identity, powerful policy, transparent TLS encryption, authentication and authorization to protect your services and data.
Mutual TLS
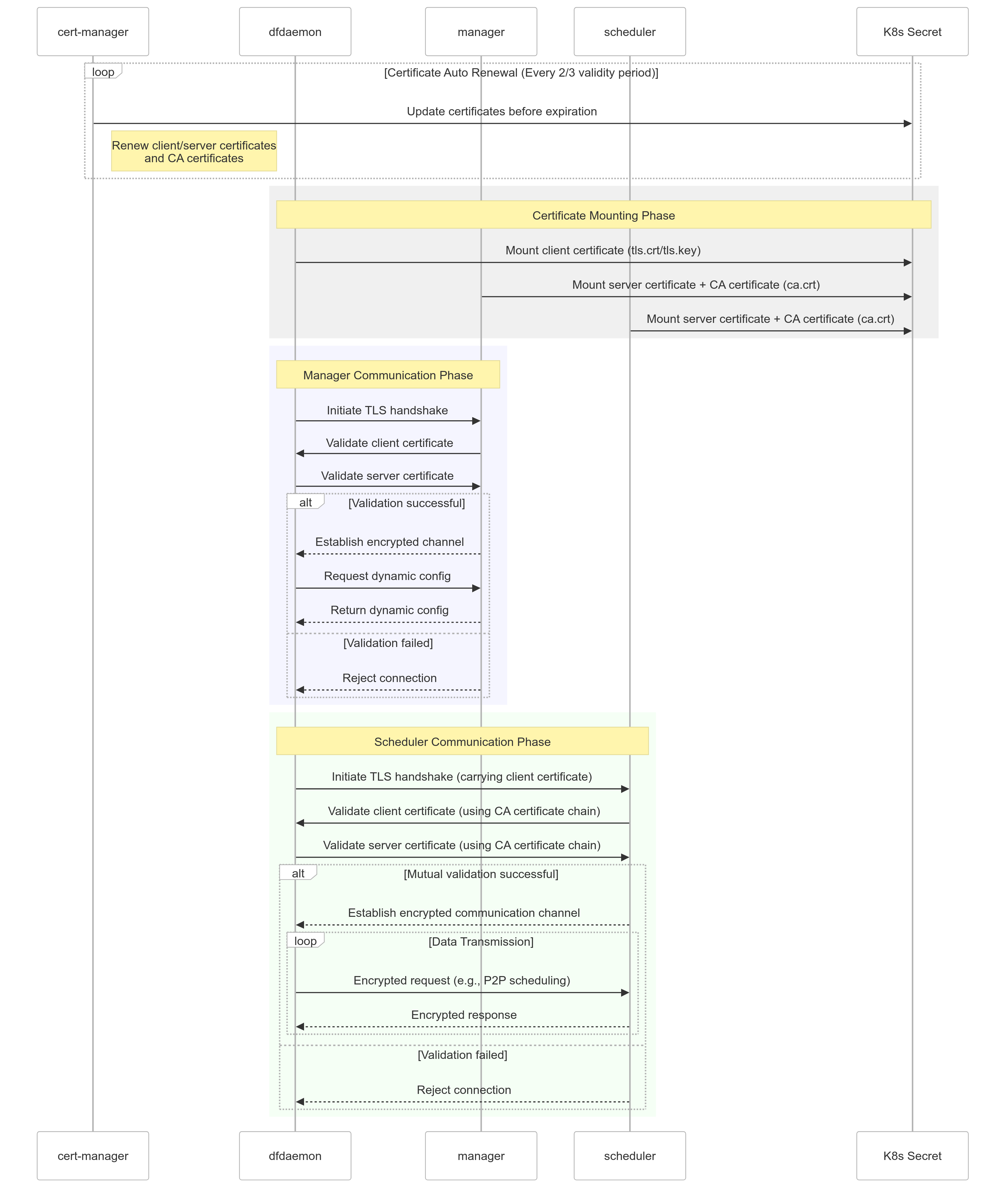
- Cert-manager will generate a self-signed CA certificate and a server certificate signed by the CA certificate.
- Cert-manager will automatically renew the CA certificate and server certificate every 2/3 of their validity period.
- Dfdaemon/manager/scheduler will mount the CA certificate and server certificate from the K8s Secret.
- Before dfdaemon connects to manager or scheduler, the two side will initiate a TLS handshake with mutual validation.
- After TLS handshake, the two side will establish encrypted channel.
Manager Console
Console HTTPS support
If you need to use HTTPS for the manager console, you must configure the certificate.
Configure manager.yaml, the default path is /etc/dragonfly/manager.yaml,
refer to manager config.
Notice: It is recommended to use
HTTPS.
server:
rest:
# REST server tls configuration.
tls:
# Certificate file path.
cert: server.crt
# Key file path.
key: server.pem
Json Web Token (JWT) for Signining
You can configure the JWT for signing in the manager console. Configure manager.yaml,
the default path is /etc/dragonfly/manager.yaml, refer to
manager config.
# Auth configuration.
auth:
# JWT configuration used for sigining.
jwt:
# Realm name to display to the user, default value is Dragonfly.
realm: 'Dragonfly'
# Key is secret key used for signing, default value is
# encoded base64 of dragonfly.
# Please change the key in production.
key: 'ZHJhZ29uZmx5Cg=='
# Timeout is duration that a jwt token is valid,
# default duration is two days.
timeout: 48h
# MaxRefresh field allows clients to refresh their token
# until MaxRefresh has passed, default duration is two days.
maxRefresh: 48h
Job
Preheat with Self-Signed Certificate
When preheating the image, dragonfly needs to call the container registry to get the image manifest.
If container regsitry is configured with a self-signed certificate, then dragonfly must be configured
with a self-signed certificate. Configure manager.yaml,
the default path is /etc/dragonfly/manager.yaml, refer to
manager config.
# Job configuration.
job:
# Preheat configuration.
preheat:
tls:
# insecureSkipVerify controls whether a client verifies the server's certificate chain and hostname.
insecureSkipVerify: false
# caCert is the CA certificate for preheat tls handshake, it can be path or PEM format string.
caCert: ca.crt
Peer's HTTP proxy
Peer's HTTP proxy has several security options that you need to configure according to the following documentation.
- connections over TLS (SSL/HTTPS)
- username+password basic-auth credentials
HTTPS support
If you need to use HTTPS proxy, you must configure the certificate,
certificate authentication can be used simultaneously with Basic Authentication
in order to provide a two levels authentication.
Configure dfdaemon.yaml, the default path is /etc/dragonfly/dfdaemon.yaml,
refer to dfdaemon config.
Notice: It is recommended to use
HTTPS.
proxy:
# caCert is the root CA cert path with PEM format for the proxy server to generate the server cert.
# If ca_cert is empty, proxy will generate a smaple CA cert by rcgen::generate_simple_self_signed.
# When client requests via the proxy, the client should not verify the server cert and set
# insecure to true. If ca_cert is not empty, proxy will sign the server cert with the CA cert. If openssl is installed,
# you can use openssl to generate the root CA cert and make the system trust the root CA cert.
# Then set the ca_cert and ca_key to the root CA cert and key path. Dfdaemon generates the server cert
# and key, and signs the server cert with the root CA cert. When client requests via the proxy,
# the proxy can intercept the request by the server cert.
caCert: 'ca.crt'
# caKey is the root CA key path with PEM format for the proxy server to generate the server cert.
# If ca_key is empty, proxy will generate a smaple CA key by rcgen::generate_simple_self_signed.
# When client requests via the proxy, the client should not verify the server cert and set
# insecure to true. If ca_key is not empty, proxy will sign the server cert with the CA cert. If openssl is installed,
# you can use openssl to generate the root CA cert and make the system trust the root CA cert.
# Then set the ca_cert and ca_key to the root CA cert and key path. Dfdaemon generates the server cert
# and key, and signs the server cert with the root CA cert. When client requests via the proxy,
# the proxy can intercept the request by the server cert.
caKey: 'ca.key'
Basic Auth
Using Basic Auth validation in Peer's HTTP Proxy.
Please note that Basic Auth is not the most secure access control technique.
Configure dfdaemon.yaml, the default path is /etc/dragonfly/dfdaemon.yaml,
refer to dfdaemon config.
proxy:
# basic_auth is the basic auth configuration for HTTP proxy in dfdaemon. If basic_auth is not
# empty, the proxy will use the basic auth to authenticate the client by Authorization
# header. The value of the Authorization header is "Basic base64(username:password)", refer
# to https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basic_access_authentication.
basicAuth:
# username is the username for basic auth.
username: 'admin'
# password is the password for basic auth.
password: 'dragonfly'
DDoS attacks
DDoS is where an attacker uses multiple sources, such as distributed groups of malware infected computers, routers, IoT devices and other endpoints to orchestrate an attack against a target, preventing legitimate users from accessing the target.
According to analysis of Dragonfly architecture, DDoS attackers can be divided into the following types:
-
Consumes the bandwidth of target network or service.
-
Send a massive amount of traffic to the target network with the goal of consuming so much bandwidth that users are denied access.
-
Bandwitdh depletion attack: Flood Attack and Amplification attack.
What can Dragonfly do against DDoS attacks?
Dragonfly implements bandwidth and request limiting to effectively mitigate the impact of attacks and ensure system stability. Please refer to Rate limit.
Observability
Monitoring
Monitoring is the process of collecting, analyzing and acting on metrics. Monitoring is a key practice in observability, as it provides the data needed to understand the state of the system and the impact of changes, refer to Monitoring.
Tracing
Tracing is a specialized form of monitoring that focuses on the flow of requests through a system. Tracing can help you understand the performance of your system and identify bottlenecks and failures, refer to Tracing.