Triton Server
This document will help you experience how to use Dragonfly with TritonServe. During the downloading of models, the file size is large and there are many services downloading the files at the same time. The bandwidth of the storage will reach the limit and the download will be slow.
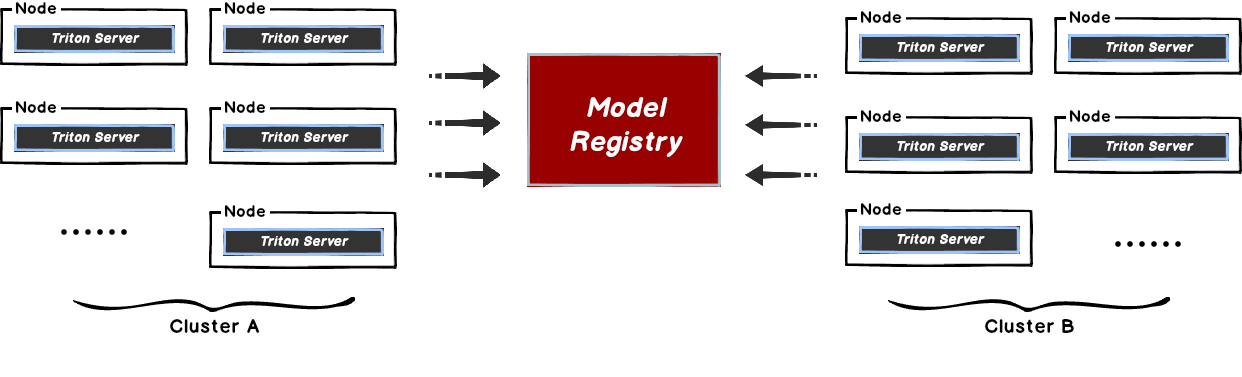
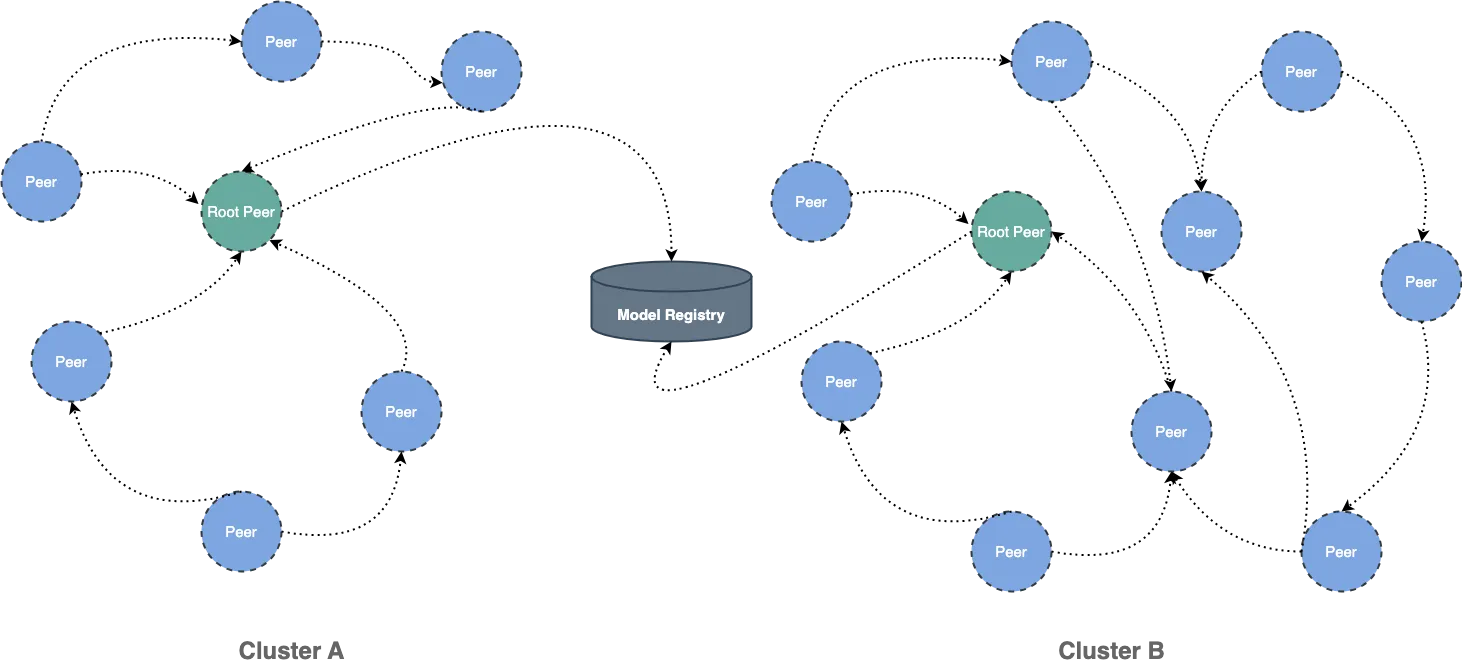
Dragonfly can be used to eliminate the bandwidth limit of the storage through P2P technology, thereby accelerating file downloading.
Installation
By integrating Dragonfly Repository Agent into Triton, download traffic through Dragonfly to pull models stored in S3, OSS, GCS, and ABS, and register models in Triton. The Dragonfly Repository Agent is in the dragonfly-repository-agent repository.
Prerequisites
| Name | Version | Document |
|---|---|---|
| Kubernetes cluster | 1.20+ | kubernetes.io |
| Helm | 3.8.0+ | helm.sh |
| Triton Server | 23.08-py3 | Triton Server |
Dragonfly Kubernetes Cluster Setup
For detailed installation documentation, please refer to quick-start-kubernetes.
Prepare Kubernetes Cluster
Kind is recommended if no kubernetes cluster is available for testing.
Create kind multi-node cluster configuration file kind-config.yaml, configuration content is as follows:
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
nodes:
- role: control-plane
- role: worker
- role: worker
Create a kind multi-node cluster using the configuration file:
kind create cluster --config kind-config.yaml
Switch the context of kubectl to kind cluster:
kubectl config use-context kind-kind
Kind loads Dragonfly image
Pull Dragonfly latest images:
docker pull dragonflyoss/scheduler:latest
docker pull dragonflyoss/manager:latest
docker pull dragonflyoss/client:latest
Kind cluster loads Dragonfly latest images:
kind load docker-image dragonflyoss/scheduler:latest
kind load docker-image dragonflyoss/manager:latest
kind load docker-image dragonflyoss/client:latest
Create Dragonfly cluster based on helm charts
Create helm charts configuration file charts-config.yaml and set
client.config.proxy.rules.regex to match the download path of the object storage.
Example: add regex:.*models.* to match download request from object storage bucket models.
Configuration content is as follows:
manager:
image:
repository: dragonflyoss/manager
tag: latest
metrics:
enable: true
scheduler:
image:
repository: dragonflyoss/scheduler
tag: latest
metrics:
enable: true
seedClient:
image:
repository: dragonflyoss/client
tag: latest
metrics:
enable: true
client:
image:
repository: dragonflyoss/client
tag: latest
metrics:
enable: true
config:
proxy:
server:
port: 4001
registryMirror:
addr: https://index.docker.io
rules:
- regex: blobs/sha256.*
# Proxy all http downlowd requests of model bucket path.
- regex: .*models.*
Create a Dragonfly cluster using the configuration file:
$ helm repo add dragonfly https://dragonflyoss.github.io/helm-charts/
$ helm install --wait --create-namespace --namespace dragonfly-system dragonfly dragonfly/dragonfly -f charts-config.yaml
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon June 27 19:56:34 2024
NAMESPACE: dragonfly-system
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
1. Get the scheduler address by running these commands:
export SCHEDULER_POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace dragonfly-system -l "app=dragonfly,release=dragonfly,component=scheduler" -o jsonpath={.items[0].metadata.name})
export SCHEDULER_CONTAINER_PORT=$(kubectl get pod --namespace dragonfly-system $SCHEDULER_POD_NAME -o jsonpath="{.spec.containers[0].ports[0].containerPort}")
kubectl --namespace dragonfly-system port-forward $SCHEDULER_POD_NAME 8002:$SCHEDULER_CONTAINER_PORT
echo "Visit http://127.0.0.1:8002 to use your scheduler"
2. Get the dfdaemon port by running these commands:
export DFDAEMON_POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace dragonfly-system -l "app=dragonfly,release=dragonfly,component=dfdaemon" -o jsonpath={.items[0].metadata.name})
export DFDAEMON_CONTAINER_PORT=$(kubectl get pod --namespace dragonfly-system $DFDAEMON_POD_NAME -o jsonpath="{.spec.containers[0].ports[0].containerPort}")
You can use $DFDAEMON_CONTAINER_PORT as a proxy port in Node.
3. Configure runtime to use dragonfly:
https://d7y.io/docs/getting-started/quick-start/kubernetes/
4. Get Jaeger query URL by running these commands:
export JAEGER_QUERY_PORT=$(kubectl --namespace dragonfly-system get services dragonfly-jaeger-query -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].port}")
kubectl --namespace dragonfly-system port-forward service/dragonfly-jaeger-query 16686:$JAEGER_QUERY_PORT
echo "Visit http://127.0.0.1:16686/search?limit=20&lookback=1h&maxDuration&minDuration&service=dragonfly to query download events"
Check that Dragonfly is deployed successfully:
$ kubectl get pods -n dragonfly-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
dragonfly-client-qhkn8 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-client-qzcz9 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-manager-6bc4454d94-ldsk7 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-mysql-0 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-redis-master-0 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-redis-replicas-0 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-redis-replicas-1 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-redis-replicas-2 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-scheduler-0 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-scheduler-1 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-scheduler-2 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-seed-client-0 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-seed-client-1 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
dragonfly-seed-client-2 1/1 Running 0 21m3s
Expose the Proxy service port
Create the dfstore.yaml configuration file to expose the port on which the
Dragonfly Peer's HTTP proxy listens. The default port is 4001 and settargetPort to 4001.
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: dfstore
spec:
selector:
app: dragonfly
component: client
release: dragonfly
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 4001
targetPort: 4001
type: NodePort
Create service:
kubectl --namespace dragonfly-system apply -f dfstore.yaml
Forward request to Dragonfly Peer's HTTP proxy:
kubectl --namespace dragonfly-system port-forward service/dfstore 4001:4001
Install Dragonfly Repository Agent
Set Dragonfly Repository Agent configuration
Create the dragonfly_config.jsonconfiguration file, the configuration is as follows:
Notice: Replace the
addraddress with your actual address.
{
"proxy": "http://127.0.0.1:4001",
"header": {
},
"filter": [
"X-Amz-Algorithm",
"X-Amz-Credential&X-Amz-Date",
"X-Amz-Expires",
"X-Amz-SignedHeaders",
"X-Amz-Signature"
]
}
- proxy: The address of Dragonfly Peer's HTTP Proxy.
- header: Adds a request header to the request.
- filter: Used to generate unique tasks and filter unnecessary query parameters in the URL.
In the filter of the configuration, set different values when using different object storage:
| type | value |
|---|---|
| OSS | ["Expires","Signature","ns"] |
| S3 | ["X-Amz-Algorithm", "X-Amz-Credential", "X-Amz-Date", "X-Amz-Expires", "X-Amz-SignedHeaders", "X-Amz-Signature"] |
| OBS | ["X-Amz-Algorithm", "X-Amz-Credential", "X-Amz-Date", "X-Obs-Date", "X-Amz-Expires", "X-Amz-SignedHeaders", "X-Amz-Signature"] |
Set Model Repository configuration
Create cloud_credential.json cloud storage credential, the configuration is as follows:
{
"gs": {
"": "PATH_TO_GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS",
"gs://gcs-bucket-002": "PATH_TO_GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS_2"
},
"s3": {
"": {
"secret_key": "AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY",
"key_id": "AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID",
"region": "AWS_DEFAULT_REGION",
"session_token": "",
"profile": ""
},
"s3://s3-bucket-002": {
"secret_key": "AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY_2",
"key_id": "AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID_2",
"region": "AWS_DEFAULT_REGION_2",
"session_token": "AWS_SESSION_TOKEN_2",
"profile": "AWS_PROFILE_2"
}
},
"as": {
"": {
"account_str": "AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT",
"account_key": "AZURE_STORAGE_KEY"
},
"as://Account-002/Container": {
"account_str": "",
"account_key": ""
}
}
}
In order to pull the model through Dragonfly, the model configuration file needs to
be added following code in config.pbtxt file:
model_repository_agents
{
agents [
{
name: "dragonfly",
}
]
}
The densenet_onnx example
contains modified configuration and model file. Modified config.pbtxt such as:
name: "densenet_onnx"
platform: "onnxruntime_onnx"
max_batch_size : 0
input [
{
name: "data_0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
format: FORMAT_NCHW
dims: [ 3, 224, 224 ]
reshape { shape: [ 1, 3, 224, 224 ] }
}
]
output [
{
name: "fc6_1"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [ 1000 ]
reshape { shape: [ 1, 1000, 1, 1 ] }
label_filename: "densenet_labels.txt"
}
]
model_repository_agents
{
agents [
{
name: "dragonfly",
}
]
}
Triton Server integrates Dragonfly Repository Agent plugin
Install Triton Server with Docker
Pull dragonflyoss/dragonfly-repository-agent image which is integrated Dragonfly Repository Agent plugin
in Triton Server, refer to Dockerfile.
docker pull dragonflyoss/dragonfly-repository-agent:latest
Run the container and mount the configuration directory:
docker run --network host --rm \
-v ${path-to-config-dir}:/home/triton/ \
dragonflyoss/dragonfly-repository-agent:latest tritonserver \
--model-repository=${model-repository-path}
path-to-config-dir: The files path ofdragonfly_config.json&cloud_credential.json.model-repository-path: The path of remote model repository.
The correct output is as follows:
=============================
== Triton Inference Server ==
=============================
successfully loaded 'densenet_onnx'
I1130 09:43:22.595672 1 server.cc:604]
+------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Repository Agent | Path |
+------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| dragonfly | /opt/tritonserver/repoagents/dragonfly/libtritonrepoagent_dragonfly.so |
+------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+
I1130 09:43:22.596011 1 server.cc:631]
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Backend | Path | Config |
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| pytorch | /opt/tritonserver/backends/pytorch/libtriton_pytorch.so | {} |
| onnxruntime | /opt/tritonserver/backends/onnxruntime/libtriton_onnxruntime.so | {"cmdline":{"auto-complete-config":"true","backend-directory":"/opt/tritonserver/backends","min-compute-capability":"6.000000","default-max-batch-size":"4"}} |
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
I1130 09:43:22.596112 1 server.cc:674]
+---------------+---------+--------+
| Model | Version | Status |
+---------------+---------+--------+
| densenet_onnx | 1 | READY |
+---------------+---------+--------+
I1130 09:43:22.598318 1 metrics.cc:703] Collecting CPU metrics
I1130 09:43:22.599373 1 tritonserver.cc:2435]
+----------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Option | Value |
+----------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| server_id | triton |
| server_version | 2.37.0 |
| server_extensions | classification sequence model_repository model_repository(unload_dependents) schedule_policy model_configuration system_shared_memory cuda_shared_memory binary_tensor_data parameters statistics trace logging |
| model_repository_path[0] | s3://192.168.36.128:9000/models |
| model_control_mode | MODE_NONE |
| strict_model_config | 0 |
| rate_limit | OFF |
| pinned_memory_pool_byte_size | 268435456 |
| min_supported_compute_capability | 6.0 |
| strict_readiness | 1 |
| exit_timeout | 30 |
| cache_enabled | 0 |
+----------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
I1130 09:43:22.610334 1 grpc_server.cc:2451] Started GRPCInferenceService at 0.0.0.0:8001
I1130 09:43:22.612623 1 http_server.cc:3558] Started HTTPService at 0.0.0.0:8000
I1130 09:43:22.695843 1 http_server.cc:187] Started Metrics Service at 0.0.0.0:8002
Execute the following command to check the Dragonfly logs:
# Find pod name.
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace dragonfly-system -l "app=dragonfly,release=dragonfly,
component=client" -o=jsonpath='{.items[?(@.spec.nodeName=="kind-worker")].metadata.name}' | head -n 1 )
# Check logs.
kubectl -n dragonfly-system exec -it ${POD_NAME} -- grep "download task succeeded" /var/log/dragonfly/dfdaemon/*
The expected output is as follows:
{
2024-04-19T02:44:09.259458Z "INFO"
"download_task":"dragonfly-client/src/grpc/dfdaemon_download.rs:276":: "download task succeeded"
"host_id": "172.18.0.3-kind-worker",
"task_id": "a46de92fcb9430049cf9e61e267e1c3c9db1f1aa4a8680a048949b06adb625a5",
"peer_id": "172.18.0.3-kind-worker-86e48d67-1653-4571-bf01-7e0c9a0a119d"
}
Verify
Call inference API:
docker run -it --rm --net=host nvcr.io/nvidia/tritonserver:23.08-py3-sdk /workspace/install/bin/image_client -m densenet_onnx -c 3 -s INCEPTION /workspace/images/mug.jpg
Check the response successful:
Request 01
Image '/workspace/images/mug.jpg':
15.349563 (504) = COFFEE MUG
13.227461 (968) = CUP
10.424893 (505) = COFFEEPOT
Performance testing
Test the performance of single-machine model download by Triton API after the integration of Dragonfly P2P. Due to the influence of the network environment of the machine itself, the actual download time is not important, but The proportion of download speed in different scenarios is more meaningful:
- Triton API: Use signed URL provided by Object Storage to download the model directly.
- Triton API & Dragonfly Cold Boot: Use
Triton Serve APIto download model via Dragonfly P2P network and no cache hits. - Hit Remote Peer: Use
Triton Serve APIto download model via Dragonfly P2P network and hit the remote peer cache. - Hit Local Peer: Use
Triton Serve APIto download model via Dragonfly P2P network and hit the local peer cache.
Test results show Triton and Dragonfly integration. It can effectively reduce the file download time. Note that this test was a single-machine test, which means that in the case of cache hits, the performance limitation is on the disk. If Dragonfly is deployed on multiple machines for P2P download, the models download speed will be faster.