eStargz
This document will help you experience how to use Dragonfly with eStargz.
Prerequisites
| Name | Version | Document |
|---|---|---|
| Kubernetes cluster | 1.20+ | kubernetes.io |
| Helm | 3.8.0+ | helm.sh |
| containerd | v1.4.3+ | containerd.io |
| Nerdctl | 0.22+ | containerd/nerdctl |
Dragonfly Kubernetes Cluster Setup
For detailed installation documentation based on kubernetes cluster, please refer to quick-start-kubernetes.
Setup kubernetes cluster
Kind is recommended if no Kubernetes cluster is available for testing.
Create kind multi-node cluster configuration file kind-config.yaml, configuration content is as follows:
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
nodes:
- role: control-plane
- role: worker
extraPortMappings:
- containerPort: 30950
hostPort: 4001
- containerPort: 30951
hostPort: 4003
- role: worker
Create a kind multi-node cluster using the configuration file:
kind create cluster --config kind-config.yaml
Switch the context of kubectl to kind cluster:
kubectl config use-context kind-kind
Kind loads Dragonfly image
Pull Dragonfly latest images:
docker pull dragonflyoss/scheduler:latest
docker pull dragonflyoss/manager:latest
docker pull dragonflyoss/client:latest
Kind cluster loads Dragonfly latest images:
kind load docker-image dragonflyoss/scheduler:latest
kind load docker-image dragonflyoss/manager:latest
kind load docker-image dragonflyoss/client:latest
Create Dragonfly cluster based on helm charts
Create helm charts configuration file charts-config.yaml and enable prefetching, configuration content is as follows:
manager:
image:
repository: dragonflyoss/manager
tag: latest
metrics:
enable: true
scheduler:
image:
repository: dragonflyoss/scheduler
tag: latest
metrics:
enable: true
seedClient:
image:
repository: dragonflyoss/client
tag: latest
metrics:
enable: true
config:
proxy:
prefetch: true
client:
image:
repository: dragonflyoss/client
tag: latest
hostNetwork: true
metrics:
enable: true
config:
proxy:
prefetch: true
server:
port: 4001
registryMirror:
addr: https://index.docker.io
rules:
- regex: blobs/sha256.*
Create a Dragonfly cluster using the configuration file:
$ helm repo add dragonfly https://dragonflyoss.github.io/helm-charts/
$ helm install --wait --create-namespace --namespace dragonfly-system dragonfly dragonfly/dragonfly -f charts-config.yaml
NAME: dragonfly
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon May 28 20:52:12 2024
NAMESPACE: dragonfly-system
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
1. Get the scheduler address by running these commands:
export SCHEDULER_POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace dragonfly-system -l "app=dragonfly,release=dragonfly,component=scheduler" -o jsonpath={.items[0].metadata.name})
export SCHEDULER_CONTAINER_PORT=$(kubectl get pod --namespace dragonfly-system $SCHEDULER_POD_NAME -o jsonpath="{.spec.containers[0].ports[0].containerPort}")
kubectl --namespace dragonfly-system port-forward $SCHEDULER_POD_NAME 8002:$SCHEDULER_CONTAINER_PORT
echo "Visit http://127.0.0.1:8002 to use your scheduler"
2. Get the dfdaemon port by running these commands:
export DFDAEMON_POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace dragonfly-system -l "app=dragonfly,release=dragonfly,component=dfdaemon" -o jsonpath={.items[0].metadata.name})
export DFDAEMON_CONTAINER_PORT=$(kubectl get pod --namespace dragonfly-system $DFDAEMON_POD_NAME -o jsonpath="{.spec.containers[0].ports[0].containerPort}")
You can use $DFDAEMON_CONTAINER_PORT as a proxy port in Node.
3. Configure runtime to use dragonfly:
https://d7y.io/docs/getting-started/quick-start/kubernetes/
Check that Dragonfly is deployed successfully:
$ kubectl get po -n dragonfly-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
dragonfly-client-5vtn2 1/1 Running 0 74m
dragonfly-client-g648f 1/1 Running 0 74m
dragonfly-manager-58ff696785-kjl8r 1/1 Running 0 74m
dragonfly-mysql-0 1/1 Running 0 74m
dragonfly-redis-master-0 1/1 Running 0 74m
dragonfly-redis-replicas-0 1/1 Running 0 74m
dragonfly-redis-replicas-1 1/1 Running 0 72m
dragonfly-redis-replicas-2 1/1 Running 0 72m
dragonfly-scheduler-0 1/1 Running 0 74m
dragonfly-scheduler-1 1/1 Running 0 66m
dragonfly-scheduler-2 1/1 Running 0 65m
dragonfly-seed-client-0 1/1 Running 4 (66m ago) 74m
dragonfly-seed-client-1 1/1 Running 0 65m
dragonfly-seed-client-2 1/1 Running 0 65m
Create peer service configuration file peer-service-config.yaml, configuration content is as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: peer
namespace: dragonfly-system
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: http-4001
nodePort: 30950
port: 4001
- name: http-4003
nodePort: 30951
port: 4003
selector:
app: dragonfly
component: client
release: dragonfly
Create a peer service using the configuration file:
kubectl apply -f peer-service-config.yaml
Install Stargz Snapshotter for containerd with Systemd
For detailed stargz installation documentation based on containerd environment, please refer to
stargz-setup-for-containerd-environment.
The example uses Systemd to manage the stargz-snapshotter service.
From the Binary Releases
Download containerd-stargz-grpc binary, please refer to stargz-snapshotter/releases:
Notice:
stargz-snapshotter_versionis recommended to use the latest version.
STARGZ_SNAPSHOTTER_VERSION=<your_stargz-snapshotter_version>
wget -O stargz-snapshotter-linux-arm64.tgz https://github.com/containerd/stargz-snapshotter/releases/download/v$STARGZ_SNAPSHOTTER_VERSION/stargz-snapshotter-v$STARGZ_SNAPSHOTTER_VERSION-linux-arm64.tar.gz
Untar the package:
# Install containerd-stargz-grpc and ctr-remote tools to /usr/local/bin.
tar -C /usr/local/bin -xvf stargz-snapshotter-linux-arm64.tgz containerd-stargz-grpc ctr-remote
Install Stargz Snapshotter plugin for containerd
Modify your config.toml (default location: /etc/containerd/config.toml), refer to configure-and-start-containerd.
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd]
snapshotter = "stargz"
disable_snapshot_annotations = false
[proxy_plugins]
[proxy_plugins.stargz]
type = "snapshot"
address = "/run/containerd-stargz-grpc/containerd-stargz-grpc.sock"
Restart containerd:
sudo systemctl restart containerd
Check that containerd uses the stargz-snapshotter plugin:
$ ctr -a /run/containerd/containerd.sock plugin ls | grep stargz
io.containerd.snapshotter.v1 stargz - ok
Systemd starts Stargz Snapshotter
Create the Stargz configuration file config.toml.
Please refer to the
Stargz Mirror
documentation for details.
Set the host address in the configuration file to your actual address. Configuration content is as follows:
[[resolver.host."docker.io".mirrors]]
host = "http://127.0.0.1:4001"
insecure = true
[resolver.host."docker.io".mirrors.header]
X-Dragonfly-Registry = ["https://index.docker.io"]
Copy configuration file to /etc/containerd-stargz-grpc/config.toml:
sudo mkdir /etc/containerd-stargz-grpc && cp config.toml /etc/containerd-stargz-grpc/config.toml
Download systemd configuration file stargz-snapshotter.service of stargz snapshotter, configuration content is as follows:
wget -O /etc/systemd/system/stargz-snapshotter.service https://raw.githubusercontent.com/containerd/stargz-snapshotter/main/script/config/etc/systemd/system/stargz-snapshotter.service
systemctl enable --now stargz-snapshotter
systemctl restart containerd
Convert an image to Stargz image
Convert alpine:3.19 image to Stargz image.
Login to Dockerhub:
docker login
Convert alpine:3.19 image to Stargz image, and DOCKERHUB_REPO_NAME environment variable
needs to be set to the user's image repository:
DOCKERHUB_REPO_NAME=<your_dockerhub_repo_name>
sudo nerdctl pull alpine:3.19
sudo nerdctl image convert --estargz --oci alpine:3.19 $DOCKERHUB_REPO_NAME/alpine:3.19-esgz
sudo nerdctl image push $DOCKERHUB_REPO_NAME/alpine:3.19-esgz
Stargz downloads images through Dragonfly
Running alpine:3.19-esgz with nerdctl:
sudo nerdctl --snapshotter stargz run --rm -it $DOCKERHUB_REPO_NAME/alpine:3.19-esgz
Verify
Check that Stargz is downloaded via Dragonfly based on mirror mode:
$ journalctl -u stargz-snapshotter | grep 'prepared remote snapshot'
containerd-stargz-grpc[4049]: {"key":"default/73/extract-656625708-vmlX sha256:7c7f00c83139c0b82eae3452058c975fb5a086d1c7d9124c77dd7a66d499dc6a","level":"debug","msg":"prepared remote snapshot","parent":"default/72/sha256:413f24977d4a9ef3a4582e041dbf50a3d32f5f60d97c98225eb492883d9c4c75","remote-snapshot-prepared":"true","time":"2024-05-30T14:36:55.660116292Z"}
You can execute the following command to check if the alpine:3.19 image is distributed via Dragonfly.
# Find pod name.
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace dragonfly-system -l "app=dragonfly,release=dragonfly,component=client" -o=jsonpath='{.items[?(@.spec.nodeName=="kind-worker")].metadata.name}' | head -n 1 )
# Find task id.
export TASK_ID=$(kubectl -n dragonfly-system exec ${POD_NAME} -- sh -c "grep -hoP 'alpine.*task_id=\"\K[^\"]+' /var/log/dragonfly/dfdaemon/* | head -n 1")
# Check logs.
kubectl -n dragonfly-system exec -it ${POD_NAME} -- sh -c "grep ${TASK_ID} /var/log/dragonfly/dfdaemon/* | grep 'download task succeeded'"
The expected output is as follows:
{
2024-04-19T02:44:09.259458Z "INFO"
"download_task":"dragonfly-client/src/grpc/dfdaemon_download.rs:276":: "download task succeeded"
"host_id": "172.18.0.3-kind-worker",
"task_id": "a46de92fcb9430049cf9e61e267e1c3c9db1f1aa4a8680a048949b06adb625a5",
"peer_id": "172.18.0.3-kind-worker-86e48d67-1653-4571-bf01-7e0c9a0a119d"
}
Performance testing
Test the performance of single-machine image download after the integration of
Stargz Mirror mode and Dragonfly P2P.
Test running version commands using images in different languages.
For example, the startup command used to run a python image is python -V.
The tests were performed on the same machine.
Due to the influence of the network environment of the machine itself,
the actual download time is not important, but the ratio of the increase in
the download time in different scenarios is very important.
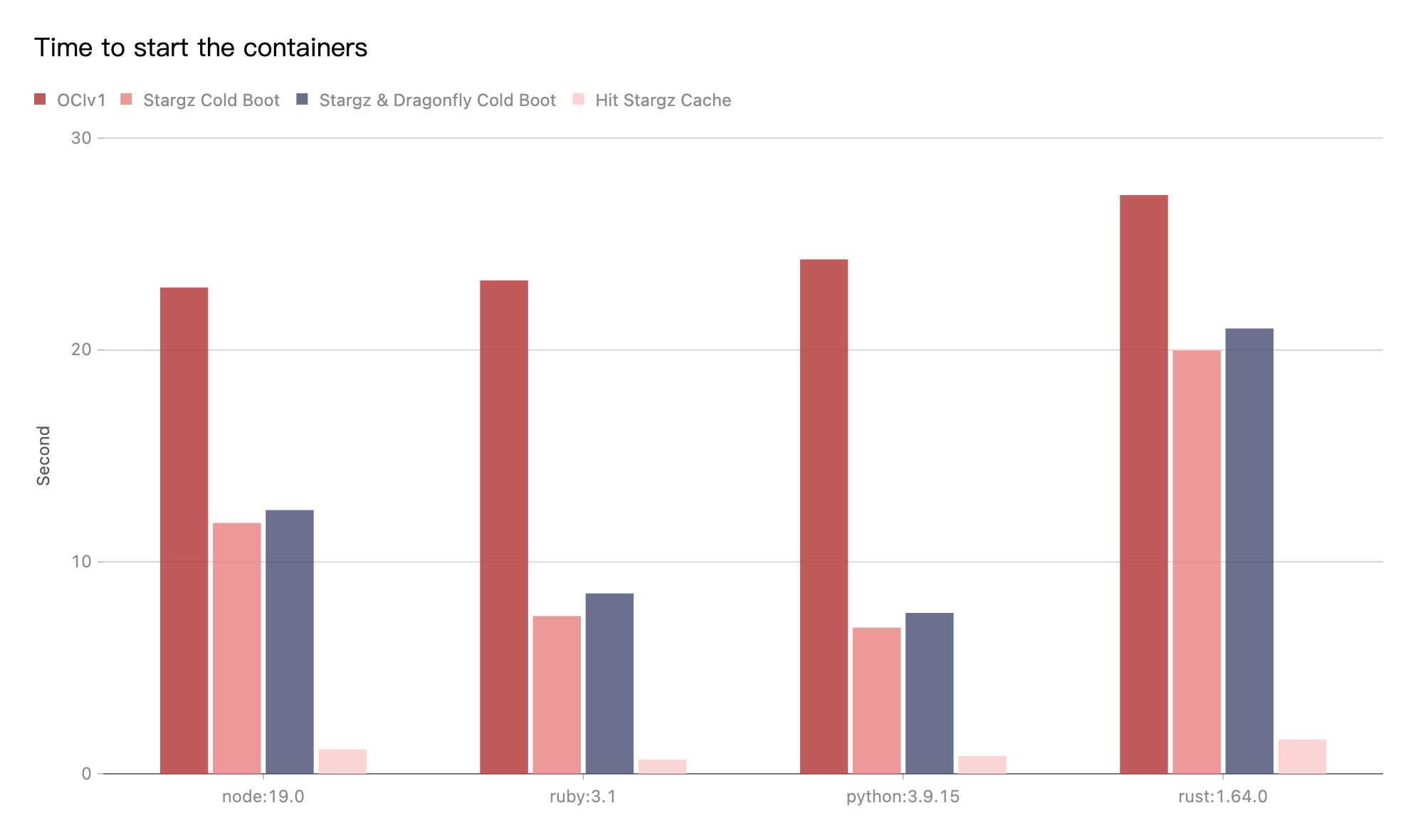
- OCIv1: Use containerd to pull image directly.
- Stargz Cold Boot: Use containerd to pull image via stargz-snapshotter and doesn't hit any cache.
- Stargz & Dragonfly Cold Boot: Use containerd to pull image via stargz-snapshotter. Transfer the traffic to Dragonfly P2P based on Stargz mirror mode and no cache hits.
Test results show Stargz Mirror mode and Dragonfly P2P integration.
Use the Stargz download image to compare the OCIv1 mode,
It can effectively reduce the image download time.
The cold boot of Stargz and Stargz & Dragonfly are basically close.
The most important thing is that if a very large kubernetes cluster uses Stargz to pull images.
The download of each image layer will be generate as many range requests as needed.
The QPS of the source of the registry is too high.
Causes the QPS of the registry to be relatively high.
Dragonfly can effectively reduce the number of requests and
download traffic for back-to-source registry.
In the best case, Dragonfly can make the same task back-to-source download only once.